Deep Vein Thrombosis
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
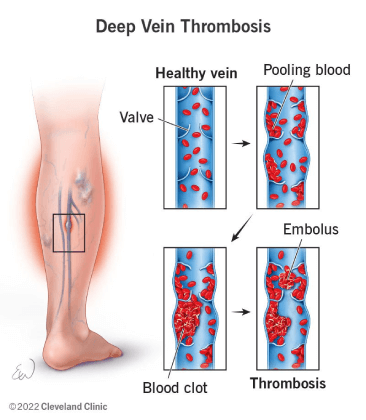
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is the development of a blood clot (thrombus) in a deep vein, typically in the legs. It may cause swelling, pain, and redness in the affected area. Although some individuals with DVT show no symptoms, it can lead to severe complications if the clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (PE).
Causes and Risk Factors
- Immobility: Extended periods of sitting or bed rest, such as after surgery or during long flights.
- Injury or surgery: Damage to veins caused by trauma or surgical procedures.
- Medical conditions: Disorders like cancer, heart failure, or clotting abnormalities.
- Medications: Use of hormonal therapy or oral contraceptives.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking or being overweight.
- Pregnancy: Increased clotting tendency and pressure on pelvic veins.
Symptoms
- Swelling in one leg (rarely in both).
- Pain or tenderness in the leg, especially during standing or walking.
- Skin that feels warm to the touch.
- Redness or discoloration over the affected area.
- Enlarged or more prominent veins.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: Evaluates swelling, tenderness, and discoloration.
- Ultrasound : A key imaging test to detect the presence of a clot.
- D-dimer Test : A blood test that identifies clot breakdown products.
- Venography or MRI : Advanced imaging methods used in specific cases to visualize clots.
Prevention
- Stay active : Engage in regular movement during travel or after surgery.
- Compression devices : Often used for hospitalized or post-surgical patients.
- Hydration : Maintaining proper hydration helps reduce blood viscosity.
- Medications : Prophylactic anticoagulants are recommended for individuals at high risk.
If left untreated, DVT can result in serious complications, such as chronic venous insufficiency or post-thrombotic syndrome, and potentially life-threatening conditions like pulmonary embolism. Early recognition and timely treatment are essential.
About the treatment
- Anticoagulation Therapy (Blood Thinners): Common medications include Heparin, Warfarin, Apixaban, and Rivaroxaban. These help prevent the growth of existing clots and reduce the risk of forming new ones.
- Compression Stockings: Used to reduce swelling and prevent post-thrombotic syndrome.
- Thrombolysis or Thrombectomy: Recommended for severe cases or large blood clots.
- Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter: A device that prevents clots from traveling to the lungs, specifically for patients who are unable to take anticoagulants.
Schedule Your Health Consultation Today
Schedule your next appointment with us quickly and effortlessly.